| Common Woodworm Types |
How to Identify the Most Common Types of Woodworm in the UK
See Also: Uncommon types of Woodworm
The term “woodworm” is slightly misleading as it does not actually refer to a type of worm, but rather the larval stage of many kinds of wood boring beetles. These larvae feed on and live in wood until they grow into an adult beetle, and then they chew their way out of the wood, and emerge to mate. Here we will document the distinguishing features of the four most common woodworm types.
 It is important to try to catch an infestation of woodworm early as it can lead to the deterioration of the integrity of the wood. The presence of small holes in the wood or the accumulation of frass are good indications of a woodworm infestation if you can see the wood in question. Much of the wood in our properties, however, is hidden from sight. Another important way to identify a woodworm infestation is by spotting the adult beetles which emerge. This happens between May and September.
It is important to try to catch an infestation of woodworm early as it can lead to the deterioration of the integrity of the wood. The presence of small holes in the wood or the accumulation of frass are good indications of a woodworm infestation if you can see the wood in question. Much of the wood in our properties, however, is hidden from sight. Another important way to identify a woodworm infestation is by spotting the adult beetles which emerge. This happens between May and September.
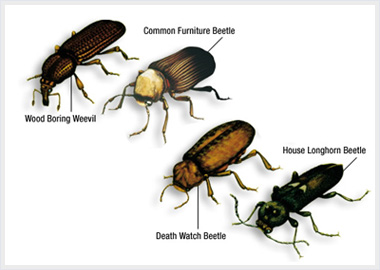
There are four common woodworm types in the UK. The two most widespread of these are the Death Watch Beetle and Common Furniture Beetle. Slightly less prevalent are the House Longhorn Beetle and Wood Boring Weevil.
The Common Furniture Beetle tends to attack the sapwood of softwoods and hardwoods, wattling and plywood. Their tunnelling tends to be quite short and goes with the grain. Exit holes are about 1 ½ to 2mm big. The adult beetle is between 2 ½ and 4 ½mm long. This is the most prevalent of the common woodworm types.
The Death Watch Beetle tends more towards the heartwood of hardwoods and rarely attacks softwoods at all. It is most commonly found in Oak. Tunnelling is extensive, meaning that the damage is often worse than it would appear from the number of holes. The exit holes are about 3mm big. The adult beetle is about 7mm long.
The House Longhorn Beetle can be very damaging. It attacks the sapwood of softwood, and frequently leaves only a veneer of firm wood behind, making the wood structurally unsound. Their emergence holes are oval rather than round, with dimensions approximately 5mm by 9mm. The adult beetle measures from about 8 to 25mm long.
The Wood Boring Weevil only attacks decaying wood. This means that if you have a problem with wood boring weevils, that is only a secondary problem, the main problem is the fungal decay of the wood. They tunnel just below the surface of the wood, along the grain. Their exit holes are very small, about 1mm, and have uneven edges. The adult beetle varies in length from about 2 ½mm to 5mm.
Do not be concerned if you cannot positively identify the species that is infesting your property; if you suspect a woodworm infestation call in a professional pest controller who will be able to survey the property and identify the type of woodworm present. It might not be one of the common woodworm types, and it might not even be one of the types that require treatment. If it does need treatment, a professional will know the best course of action to take. For more information on the less widespread species, see the “uncommon woodworm types”.
See Also: Wood Boring Weevils,
House Longhorn Beetle,
Death Watch Beetle
|
| |
|
|
|